FullStack Next.js & Django Authentication: Django REST, TypeScript, JWT, Wretch & Djoser
If you're a software engineer, especially a full-stack developer, your job involves merging different technologies—like backend and frontend—to build applications. This guide is tailored for developers familiar with Python or JavaScript, specifically those working with Django, or Next.js, or both. We'll focus on creating a backend with Django that manages authentication, which will be utilized by a frontend developed with Next.js.
While Next.js offers robust backend features, including authentication support through NextAuth, Django's ecosystem brings years of development and stability, making it an excellent choice for constructing a reliable backend.
Technologies We'll Use
Django & Django REST Framework: We'll leverage these to create a REST API that our Next.js frontend will interact with.
Json Web Token (JWT): Even though it is more like an industry standard, we will use JWTs for stateless authentication in this article. If you want to learn more, you can refer to the official documentation.
Djoser: This package simplifies authentication processes like login, registration, account verification, and password resets, allowing us to avoid writing these functionalities from scratch.
Next.js: Our choice for the frontend framework. Its
AppRouterarchitecture offers innovative ways to build applications, including adding authentication.Wretch: For handling HTTP requests, we'll use
wretch, a concise fetch API wrapper. It provides an easy way to manage requests, including token refresh logic. If you preferaxios, I'll include links to resources for that as well.
What You'll Learn
Setting up authentication in a Django and Django REST backend API.
Building login, registration, and password reset functionalities and pages in Next.js.
Connecting your Django REST API with the Next.js frontend.
Managing sessions, including JWT refresh tokens in Next.js, using middleware functionality,
wretch, andswr.
Now, let's dive into the setup of our application. This guide aims to make complex concepts understandable, using simple terms and comprehensive explanations, ensuring that you're not just copying code, but also grasping the how and why behind each step.
Setting Up a Django Backend for Next.js Authentication
This guide is designed for developers working in a Linux environment, using commands specific to Linux systems. Here, we'll walk you through setting up your Django backend for Next.js authentication.
Creating the Project Directory
First, let's create a new directory for our project, which we'll call django-next-auth. You're welcome to name it anything you prefer. We'll also set up a Python development environment within this directory, using Python 3.11 for this project.
Open your terminal and run the following commands:
mkdir django-next-auth && cd django-next-auth
python3.11 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
The sequence of commands above creates a new directory, initializes a Python virtual environment, and activates it.
Installing Required Packages
With our environment ready, we'll install the necessary Python packages for our development. These include Django, Django REST Framework, Djoser for authentication, and other supportive packages.
Execute the following command to install these packages:
pip install django djangorestframework djoser djangorestframework-simplejwt django-cors-headers
Now, we're set to create our Django project. We'll name the project ApiRoot. You can create the project by running:
django-admin startproject ApiRoot .
Congratulations 🚀, your Django project is now set up! You're ready to start developing the backend for your Next.js application.
In the next section, we'll dive into configuring Django for authentication and how to connect it with a Next.js frontend.
Setting Up the Django REST API
After successfully establishing our Django project in the previous section, we're now moving on to configure the REST API, integrating JWT authentication via the Djoser package.
Djoser is a comprehensive solution for adding authentication features to a Django REST API, offering support for a wide array of functionalities including login, registration, password resets and updates, account activation, and deletion, among others.
For the scope of this article, our focus will be on implementing login, registration, password reset, and logout capabilities. We'll ensure our Django API is equipped to manage these functionalities by properly setting up Djoser.
Implementing Djoser Configuration
Djoser simplifies the process by providing a collection of ready-to-use URLs that can be seamlessly incorporated into the project's URL configurations without the need for additional coding. However, prior to integrating these URLs, it's essential to register the djoser app within the INSTALLED_APPS setting of our Django project and applying necessary adjustments in the DJOSER settings to tailor the authentication features to our needs.
# ApiRoot/settings.py
...
INSTALLED_APPS = [
"django.contrib.admin",
"django.contrib.auth",
"django.contrib.contenttypes",
"django.contrib.sessions",
"django.contrib.messages",
"django.contrib.staticfiles",
# installed apps
"rest_framework",
"djoser",
"rest_framework_simplejwt.token_blacklist",
]
In the code above, we are completing the list of apps by adding rest_framework, djoser and rest_framework_simplejwt.token_blacklist. The last one is useful as we need to add a logout feature in the application. This application is used to blacklist a refresh token and thus does not allow the client with a refresh token blacklisted to claim a new access token.
Now that the djoser application is installed, let's configure Djoser in DJOSER setting but also the REST_FRAMEWORK, SIMPLE_JWT, and EMAIL_BACKEND.
...
# ApiRoot/settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": (
"rest_framework_simplejwt.authentication.JWTAuthentication",
),
}
SIMPLE_JWT = {
"AUTH_HEADER_TYPES": ("Bearer",),
}
EMAIL_BACKEND = "django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend"
DJOSER = {
"PASSWORD_RESET_CONFIRM_URL": "auth/password/reset-password-confirmation/?uid={uid}&token={token}",
"ACTIVATION_URL": "#/activate/{uid}/{token}",
"SEND_ACTIVATION_EMAIL": False,
"SERIALIZERS": {},
}
Let's describe the code above:
REST_FRAMEWORK: This setting configures the Django REST Framework to authenticate API requests using JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) through therest_framework_simplejwt.authentication.JWTAuthenticationclass. It ensures that only requests with valid JWTs can access protected resources.SIMPLE_JWT: We adjust the JWT authentication mechanism to recognize authentication headers that start with "Bearer". This is a standard practice where the client sends a token in the formatAuthorization: Bearer <token>to authenticate API requests.EMAIL_BACKEND: It will direct Django to use the console email backend, meaning that instead of sending out emails through SMTP or another email service, email contents are printed to the console. This will be particularly useful for debugging and development in this article.DJOSER: Provides configurations for Djoser, a library that simplifies creating RESTful APIs for handling authentication tasks in Django. The settings include:PASSWORD_RESET_CONFIRM_URL: The URL template for password reset confirmation links. It contains placeholders for the user ID ({uid}) and a password reset token ({token}), which are dynamically replaced by Djoser.ACTIVATION_URL: Specifies the URL template for account activation links, similar to the password reset confirmation URL, but used for activating user accounts.SEND_ACTIVATION_EMAIL: When set toFalse, this option disables Djoser from automatically sending account activation emails upon user registration. This is useful in scenarios where automatic email sending is not desired.SERIALIZERS: Allows for the specification of custom serializers for various Djoser operations. It's left empty here, indicating the use of default serializers provided by Djoser.
Observe that the PASSWORD_RESET_CONFIRM_URL is configured to direct to auth/password/reset-password-confirmation/?uid={uid}&token={token}. This URL will be associated with a specific page within our Next.js application designed for the password reset process. Upon navigating to this page, the application will extract the user ID (uid) and the reset token (token) from the URL's query parameters to proceed with the password reset procedure.
We also need these two variables to the settings file so Django will display the site name and the correct domain in the mail sent to the user.
# ApiRoot/settings.py
...
SITE_NAME = "Test Django Next.js"
DOMAIN = 'localhost:3000'
Once the configuration is done, we can move to add the Djoser URLs to the Django application URLs. In the ApiRoot/urls.py, add djoser.urls to the list of URLs callable.
from django.urls import path, include
from auth.views import LogoutView
urlpatterns = [
path("auth/", include("djoser.urls")),
path("auth/", include("djoser.urls.jwt")),
path("auth/logout/", LogoutView.as_view()),
]
This code snippet above defines URL patterns for a Django application, specifically integrating authentication routes using Djoser and JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for authentication, along with a custom logout route:
path("auth/", include("djoser.urls")): This line includes Djoser's default URL patterns into the application's URLs under theauth/prefix. Djoser provides a set of pre-built paths for handling user authentication tasks such as registration, and password reset.path("auth/", include("djoser.urls.jwt")): Adds JWT authentication URL patterns provided by Djoser under the sameauth/prefix. These URLs are dedicated to handling JWT operations, like obtaining, refreshing, and verifying tokens.
By setting up these URL configurations, the application now has a robust authentication system in place. This system enables users to sign up, sign in, reset passwords, and securely authenticate using JWTs.
Below are the Djoser URLs we'll be utilizing in this guide:
/users/: Submitting a POST request to this route creates a new user account on the Django backend, serving as the registration process./users/me/: A GET request to this endpoint returns information about the currently authenticated user, requiring the user to be logged in./users/reset_password/: A POST request here initiates a password reset process by sending an email to the provided address with a password reset link, but only if the user account exists./users/reset_password_confirm/: By making a POST request to this route with theuid,token, andnew_password, the user can reset their password to the new value specified in thenew_passwordfield./jwt/create/: This endpoint is used for logging in, where it authenticates the user and returns a JWT for subsequent authenticated requests./jwt/refresh/: This endpoint is for refreshing an existing access token by providing a valid refresh token, thus granting a new access token.
Before considering our backend application complete, it's essential to incorporate a logout feature. Given the stateless nature of JWT authentication, the system lacks real-time knowledge regarding the expiration status of tokens. This means that the backend remains unaware of a user's authentication state until an API request is made.
This characteristic of JWTs complicates token invalidation since a token remains valid until it reaches its configured lifetime expiration.
To address this, we plan to introduce an endpoint specifically for handling refresh token invalidation. This endpoint, designated as auth/logout, will be responsible for managing the API's logout logic, effectively allowing us to invalidate tokens as part of the logout process.
Let's move to coding this endpoint.
Adding the logout endpoint
In this section, we're going to set up an endpoint using an APIView that will handle logout actions. We aim to use a feature called token blacklist, which comes from the rest_framework_simplejwt.token_blacklist Django app.
Inside this app, there's a RefreshToken class with a method named blacklist. Invoking this method on an instance created from the RefreshToken blacklists the specified refresh token. This means the refresh token can no longer be used to get new access tokens, effectively logging the user out by ending their JWT session.
At the root of the Django project, create a new Python package called auth. Inside this package create a file called views.py. This file will contain the code for the LogoutView class.
from rest_framework_simplejwt.tokens import RefreshToken
from rest_framework_simplejwt.exceptions import TokenError
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.permissions import AllowAny
from rest_framework import status
from rest_framework.response import Response
from django.core.exceptions import ObjectDoesNotExist
class LogoutView(APIView):
permission_classes = (AllowAny,)
authentication_classes = ()
def post(self, request):
try:
refresh_token = request.data["refresh"]
token = RefreshToken(refresh_token)
token.blacklist()
return Response(status=status.HTTP_200_OK)
except (ObjectDoesNotExist, TokenError):
return Response(status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
The code above defines a custom Django REST Framework view, LogoutView which inherits from APIView. The purpose of this view is to handle logout requests by blacklisting JWT refresh tokens. Here's a breakdown of the logic inside this class:
permission_classes = (AllowAny,): This line ensures that any user can attempt to log out, with authentication or not.authentication_classes = (): By setting this to an empty tuple, the view is configured not to use any of the default authentication methods for this specific request. This is important for our logout functionality, as it should be accessible without requiring a valid token for authentication.Inside the
postmethod:refresh_token =request.data["refresh"]: We attempt to retrieve the refresh token sent by the client in the request body. This token is what will be blacklisted to log the user out.token = RefreshToken(refresh_token): We create aRefreshTokenobject from the provided refresh token string. This object is provided by therest_framework_simplejwt.token_blacklistapp and is necessary for accessing the blacklist functionality.token.blacklist(): We then call theblacklistmethod on theRefreshTokenobject, adding the token to the blacklist. Once blacklisted, the token cannot be used to obtain new access tokens, effectively logging the user out.return Response(status=status.HTTP_200_OK): If the process succeeds without raising any exceptions, the server responds with a 200 OK status, indicating a successful logout.
Otherwise, we just send a
400status code stating that the logout request has failed.
This LogoutView thus provides a secure way to handle logout requests by invalidating JWT refresh tokens, ensuring that users can effectively end their sessions.
Let's add this view to the ApiRoot/urls.py file.
# ApiRoot/urls.py
...
urlpatterns = [
...
path("auth/logout/", LogoutView.as_view()),
]
Now to ensure that the application is ready to run correctly, execute the following command to run the Django migrations.
python manage.py migrate
With the authentication URLs defined, we should be able to move to the creation of the frontend and start authenticating and consuming data from the API. But wait, there is still something we need to configure, web developer's biggest opps : CORS.
Important configuration: CORS
Before the API is usable from a frontend POV, we need to configure CORS. But what are CORS? Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a security feature implemented in web browsers to control how web pages in one domain can request resources from another domain. It's an important part of web security because it helps prevent malicious attacks, such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and data theft, by restricting how resources can be shared between different origins.
In our case, making a request from the browser to the API URL will return a frontend error, a very ugly and sometimes frustrating one.
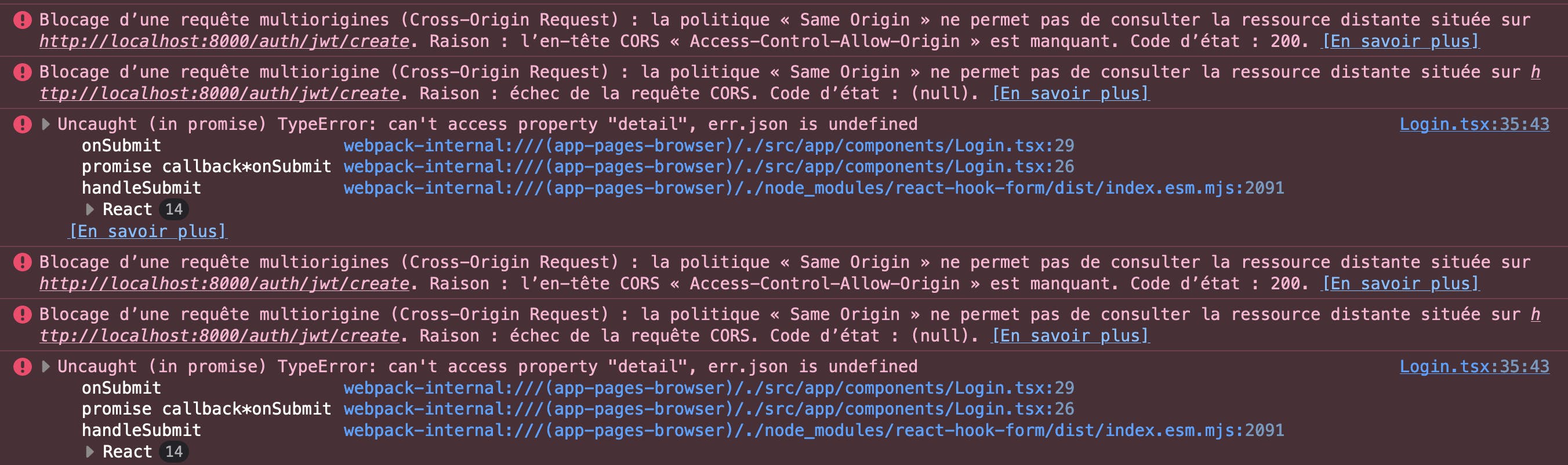
Let's solve this issue by configuring CORS on the API we have created using the django-cors-headers package.
Once the installation is done, open the settings.py file and ensure to add the following configurations.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...,
"corsheaders",
...,
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
...,
"corsheaders.middleware.CorsMiddleware",
"django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware",
...,
]
CORS_ALLOWED_ORIGINS = [
"http://localhost:3000",
"http://127.0.0.1:3000",
]
In the code above, the CORS_ALLOWED_ORIGINS helps us tell Django which domain origin to accept. As we are planning to use Next.js on the frontend and these apps run by default on the 3000 port, we are adding two addressees from which Django can let requests coming from.
Great! We have successfully built a Django REST API that supports JWT authentication and is ready to serve data.
In the next section, we will build a Next.js frontend using the App router architecture that will consume data from the Django backend we have created.
Building the frontend with Next.js
In the previous section of this article, we developed a Django and Django REST API that supports JWT authentication. We ensured that a frontend application could seamlessly communicate with the API by addressing CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) issues through configurations provided by the django-cors-headers package.
In this section, we'll focus on creating a frontend application consisting of five pages. Four of these pages will cater to authentication processes: registration, login, request for password reset, and password reset confirmation. The fifth page will be the home page, which is designed to be protected; only users who are authenticated will have access to it.
By the end of this section, you'll learn how to:
Construct a frontend application using Next.js.
Integrate this application with a REST API.
Manage JWT sessions leveraging the App router architecture in Next.js.
Setup the frontend application
The Next.js team has simplified the process of creating a new Next.js project significantly. To start a new project, execute the following command:
npx create-next-app@latest
During the setup, you'll be prompted to make several configuration choices. To align your project setup with the guidelines provided in this article, select the following options:
What is your project named? frontend
Would you like to use TypeScript? Yes
Would you like to use ESLint? Yes
Would you like to use Tailwind CSS? Yes
Would you like to use `src/` directory? Yes
Would you like to use App Router? (recommended) Yes
Would you like to customize the default import alias (@/*)? Yes
Once you are done choosing the options for the creation of the project, a new directory called frontend containing all the resources needed to develop, start, and build the Next.js project will be created.
cd frontend && npm run dev
This will start the project on http://localhost:3000.
Great! Once you've confirmed that the project is running smoothly, the next step is to install some essential packages that will be utilized throughout the project. These packages are crucial for handling HTTP requests, state management, and cookie manipulation in a more efficient and simplified manner. Run the following command in your project directory to install them:
npm install wretch swr js-cookies react-hook-form
npm install -D @types/js-cookies
Here's a brief overview of what each package offers:
wretch: A small, modern wrapper built around the fetch API that simplifies HTTP requests and error handling.swr: A React hooks library for data fetching, which allows you to fetch data with hooks efficiently and quickly. It handles caching, revalidation, focus tracking, and more out of the box.js-cookies: A simple, lightweight JavaScript API for handling cookies. It provides utility functions to make cookie manipulation easy.react-hook-form: A library to handle form validation and submission.@types/js-cookies: Type definitions forjs-cookies.
Once the project is created, make sure you have the following structure for your src/app directory.
.
├── auth
│ ├── password
│ │ ├── reset-password
│ │ │ └── page.tsx
│ │ └── reset-password-confirmation
│ │ └── page.tsx
│ ├── register
│ │ └── page.tsx
│ └── utils.ts
├── components
│ ├── Login.tsx
│ ├── Register.tsx
│ ├── ResetPassword.tsx
│ └── ResetPasswordConfirmation.tsx
├── dashboard
│ └── page.tsx
├── favicon.ico
├── fetcher.ts
├── globals.css
├── layout.tsx
└── page.tsx
This structure leverages the App Router architecture introduced by Next.js 13, offering a few key benefits for developing web applications:
Modularity: By dividing the application into distinct sections like
authfor authentication-related pages anddashboardfor user dashboard views, the project becomes more organized. This modularity makes it easier to navigate the project and manage development tasks.Page-based Routing: Next.js automatically routes files from
appdirectory using the App Router conventions. Eachpage.tsxfile represents a route based on its file path, simplifying the creation of navigable single-page applications.Reusable Components: The
componentsdirectory contains reusable UI components (Login.tsx,Register.tsx, etc.), promoting DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principles and ensuring consistency across the application. It is possible to put components in each directory for a page. So for example,auth/registercan contain theRegister.tsxcomponent. It depends on your taste and if this organization makes sense for your project.Authentication Flow Management: The
authdirectory is specifically tailored for authentication flows, including registration, password resets, and confirmations. This separation of concerns makes it easier to manage and update authentication logic independently from other parts of the application.Utility and Global Styles: Files like
fetcher.tsfor data fetching utilities that will be used alongsideswr,globals.cssfor global styles, andlayout.tsxfor a common layout component aids in maintaining a consistent look and feel, as well as providing common functionality across the application.
With the project installed, we can now move to building the component of the Next.js project, starting with the HTTP modules for requests and utils to stock tokens in a cookie.
Writing the HTTP module for authentication
In the precedent section, we have set up the frontend project to ensure that we can develop the intended features. In this section, we will write the code for the HTTP module for authentication in the src/app/auth/utils.ts file and also the fetcher that will be used alongside swr in the file src/app/fetcher.ts.
Let's start with writing the HTTP methods for handling authentication on the frontend.
// src/app/auth/utils.ts
import wretch from "wretch";
import Cookies from "js-cookie";
// Base API setup for making HTTP requests
const api = wretch("http://localhost:8000").accept("application/json");
This code initializes our base API for HTTP requests. By configuring wretch with our backend's base URL and setting the header to accept application/json, we create a foundation for all subsequent POST requests in this module.
Next, we can start writing methods that will be used to manage cookies. We will be storing access and refresh tokens inside those cookies.
Why store tokens inside cookies instead of localStorage? Storing tokens in cookies rather than localStorage offers several advantages:
Security: Cookies can be configured as HttpOnly, meaning they are inaccessible to JavaScript running in the browser. This reduces the risk of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks being able to steal the tokens.
Cross-Origin Read Blocking (CORB) Protection: Cookies adhere to the same-origin policy, offering an additional layer of security by restricting how cookies can be shared across sites.
Automatic Sending: Cookies are automatically included in every HTTP request made to the server, simplifying the process of sending tokens for authentication.
Domain and Path Restrictions: Cookies allow for fine-grained control over which domains and paths can access them, providing tighter security controls compared to
localStorage.
However, it's important to recognize that cookies have limitations regarding storage capacity. This is where utilizing a combination of cookies and localStorage becomes advantageous. By adopting this hybrid approach, you can leverage the strengths of both storage mechanisms:
Cookies can be used to store sensitive information. Their security features, such as
HttpOnlyflags, making them ideal for handling authentication tokens. Cookies ensure that sensitive data is transmitted securely between the client and server, mitigating risks associated with client-side script access.localStorage is well-suited for storing non-sensitive information. With its larger storage capacity compared to cookies, localStorage can be used to store data that doesn't require the same level of security, such as user preferences or UI theme states. This data is easily accessible by client-side scripts, making it convenient for enhancing the user experience without compromising security.
Let's now write the methods for storing tokens, retrieving tokens, and removing tokens from cookies.
// src/app/auth/utils.ts
...
/**
* Stores a token in cookies.
* @param {string} token - The token to be stored.
* @param {"access" | "refresh"} type - The type of the token (access or refresh).
*/
const storeToken = (token: string, type: "access" | "refresh") => {
Cookies.set(type + "Token", token);
};
/**
* Retrieves a token from cookies.
* @param {"access" | "refresh"} type - The type of the token to retrieve (access or refresh).
* @returns {string | undefined} The token, if found.
*/
const getToken = (type: string) => {
return Cookies.get(type + "Token");
};
/**
* Removes both access and refresh tokens from cookies.
*/
const removeTokens = () => {
Cookies.remove("accessToken");
Cookies.remove("refreshToken");
};
The Cookies object offers a suite of methods to interact with cookies, including setting, retrieving, and removing them. Here's a brief overview of how these methods work:
Cookies.setmethod: To store a value in cookies, you use this method by providing a key and the value you wish to store. This is how you can set both access and refresh tokens or any other piece of data you need to persist across sessions. It's also possible to specify additional options such as expiry, path, and domain to further control how the cookie is stored. You can learn more at https://www.npmjs.com/package/js-cookie#cookie-attributes.Cookies.getmethod: When you need to retrieve a value from the cookies, you use this method with the key as its argument. If the key exists, you'll receive the corresponding value. If the key doesn't exist in the cookies, it returnsundefined.Cookies.removemethod: To delete a key-value pair from the cookies, this method is used, again specifying the key.
With the cookies methods set, we can write the different methods for login, registration, logout, and password reset logic.
// src/app/auth/utils.ts
...
const register = (email: string, username: string, password: string) => {
return api.post({ email, username, password }, "/auth/users/");
};
const login = (email: string, password: string) => {
return api.post({ username: email, password }, "/auth/jwt/create");
};
const logout = () => {
const refreshToken = getToken("refresh");
return api.post({ refresh: refreshToken }, "/auth/logout/");
};
const handleJWTRefresh = () => {
const refreshToken = getToken("refresh");
return api.post({ refresh: refreshToken }, "/auth/jwt/refresh");
};
const resetPassword = (email: string) => {
return api.post({ email }, "/auth/users/reset_password/");
};
const resetPasswordConfirm = (
new_password: string,
re_new_password: string,
token: string,
uid: string
) => {
return api.post(
{ uid, token, new_password, re_new_password },
"/auth/users/reset_password_confirm/"
);
};
Let's explain the methods in the code above:
register: This method sends aPOSTrequest to create a new user account with the provided email, username, and password.login: Initiates aPOSTrequest to authenticate a user by sending their email and password, expecting to receive JWT tokens upon successful authentication.logout: Executes aPOSTrequest to log the user out by sending the refresh token to the server, where it will be invalidated.handleJWTRefresh: Sends aPOSTrequest with the refresh token to obtain a new access token, ensuring the user remains authenticated without re-entering credentials.resetPassword: Triggers aPOSTrequest to initiate the password reset process by sending the user's email to the server, which then sends a password reset link.resetPasswordConfirm: Completes the password reset process by sending aPOSTrequest with the new password, confirmation of the new password, token, and user ID to validate and update the user's password.
Finally, we can import these functions into another function called AuthActions.
// src/app/auth/utils.ts
...
export const AuthActions = () => {
return {
login,
resetPasswordConfirm,
handleJWTRefresh,
register,
resetPassword,
storeToken,
getToken,
logout,
removeTokens,
};
};
The AuthActions function encapsulates and exports an object containing references to the authentication-related functions. By grouping these methods under AuthActions, we can streamline the process of importing and using them throughout your project, enhancing code readability and maintainability.
We have finally written the methods for handling HTTP requests for authentication in the code. We can now write the fetcher that will be used alongside swr to make fetching HTTP requests.
In the src/app/fetcher.ts file, add the following lines of code.
// src/app/fetcher.ts
import wretch, { Wretch, WretchError } from "wretch";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
// Extract necessary functions from the AuthActions utility.
const { handleJWTRefresh, storeToken, getToken } = AuthActions();
const api = () => {
return (
wretch("http://localhost:8000")
// Initialize authentication with the access token.
.auth(`Bearer ${getToken("access")}`)
// Catch 401 errors to refresh the token and retry the request.
.catcher(401, async (error: WretchError, request: Wretch) => {
try {
// Attempt to refresh the JWT token.
const { access } = (await handleJWTRefresh().json()) as {
access: string;
};
// Store the new access token.
storeToken(access, "access");
// Replay the original request with the new access token.
return request
.auth(`Bearer ${access}`)
.fetch()
.unauthorized(() => {
window.location.replace("/");
})
.json();
} catch (err) {
window.location.replace("/");
}
})
);
};
export const fetcher = (url: string): Promise<any> => {
return api().get(url).json();
};
The code snippet above demonstrates an advanced setup for handling authentication and token refresh with wretch in the Next.js application. Let's see what is happening there:
Extract Functions: Initially, it extracts
handleJWTRefresh,storeToken, andgetTokenfrom theAuthActionsutility, making these functions available for managing JWT tokens.Configure API Requests: We define an
apifunction that configureswretchfor making authenticated requests to a backend server.Token Management in Requests: The
apifunction automatically adds an Authorization header with the access token obtained viagetToken. If a request returns a 401 Unauthorized status, indicating an expired or invalid token, it attempts to refresh the token usinghandleJWTRefresh. This is wherewretchis fabulous as it just requires a few lines of code to ensure that we can trigger the token refresh logic, using thecatchercallback. You can see an example of how to do it withaxioshere.Handle Token Refresh: Upon a successful token refresh, we store the new access token using
storeTokenand retry the original request with the updated token. If the refresh fails or the retried request is unauthorized, we redirect the user to the Login page.Fetcher Utility: Finally, we export a
fetcherfunction that wraps theapilogic for easy use withswror other data-fetching libraries. This function is designed to make GET requests to a specified URL and automatically handle token refresh and error scenarios, providing seamless integration for authenticated data fetching in the application. This is the function that we will use alongsideswr.
Great! We have written the HTTP modules needed to handle all kinds of requests within the Next.js application. In the next section, we will build the Login page.
Building the Login Page
In the precedent section, we have written all necessary HTTP functions to handle authentication but also authenticated fetching in the application. In this section, we will focus on building the Login page. We will first start by writing the Login component in src/app/components/Login.tsx and finally, add this component to the page at src/app/page.tsx.
Let's start by writing the Login component.
// src/app/components/Login.tsx
import React from "react";
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
import Link from "next/link";
type FormData = {
email: string;
password: string;
};
const Login = () => {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
setError,
} = useForm<FormData>();
const router = useRouter();
const { login, storeToken } = AuthActions();
const onSubmit = (data: FormData) => {
login(data.email, data.password)
.json((json) => {
storeToken(json.access, "access");
storeToken(json.refresh, "refresh");
router.push("dashboard");
})
.catch((err) => {
setError("root", { type: "manual", message: err.json.detail });
});
};
...
};
export default Login;
The Login.tsx component showcases how to implement a login form in a Next.js application using react-hook-form for form handling, AuthActions for authentication, and Next.js's useRouter for navigation.
Form Setup with
react-hook-form: We usereact-hook-formto manage form state, validation, and submission. We define aFormDatatype for TypeScript support, ensuring type safety for the form inputs.Authentication and Navigation: We integrate authentication logic by extracting the
loginandstoreTokenmethods fromAuthActions. Upon form submission, it attempts to log the user in with the provided email and password.Successful Login Handling: If the login is successful, we store the access and refresh tokens using
storeTokenand redirect the user to the dashboard using Next.js'srouter.pushmethod.Error Handling: In case of a login failure, we capture the error and set a form error using
setError, which can then be displayed to the user as feedback.
We can now add the JSX code handling the UI part of this component.
// src/app/components/Login.tsx
const Login = () => {
...
return (
<div className="flex items-center justify-center min-h-screen bg-gray-100">
<div className="px-8 py-6 mt-4 text-left bg-white shadow-lg w-1/3">
<h3 className="text-2xl font-semibold">Login to your account</h3>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)} className="mt-4">
<div>
<label className="block" htmlFor="email">
Email
</label>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Email"
{...register("email", { required: true })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.email && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">Email is required</span>
)}
</div>
<div className="mt-4">
<label className="block" htmlFor="password">
Password
</label>
<input
type="password"
placeholder="Password"
{...register("password", { required: true })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.password && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">Password is required</span>
)}
</div>
<div className="flex items-center justify-between mt-4">
<button className="px-12 py-2 leading-5 text-white transition-colors duration-200 transform bg-blue-600 rounded-md hover:bg-blue-700 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-700">
Login
</button>
</div>
{errors.root && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">{errors.root.message}</span>
)}
</form>
<div className="mt-6 text-center">
<Link
href="/auth/password/reset-password"
className="text-sm text-blue-600 hover:underline"
>
Forgot password?
</Link>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Login;
With the JSX code written, we can now add this component to the src/app/page.tsx file.
"use client";
import Login from "@/app/components/Login";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main>
<Login />
</main>
);
}
The use client directive tells Next.js to render the component on the client side only, leveraging Next.js's support for selective server-side rendering (SSR) and static generation (SSG) with client-side rendering capabilities.
With the JSX code above, when vising the localhost:3000 URL, you will have a similar display. 👇
With the JSX code provided, visiting the localhost:3000 URL will display a page similar to the following screenshot:
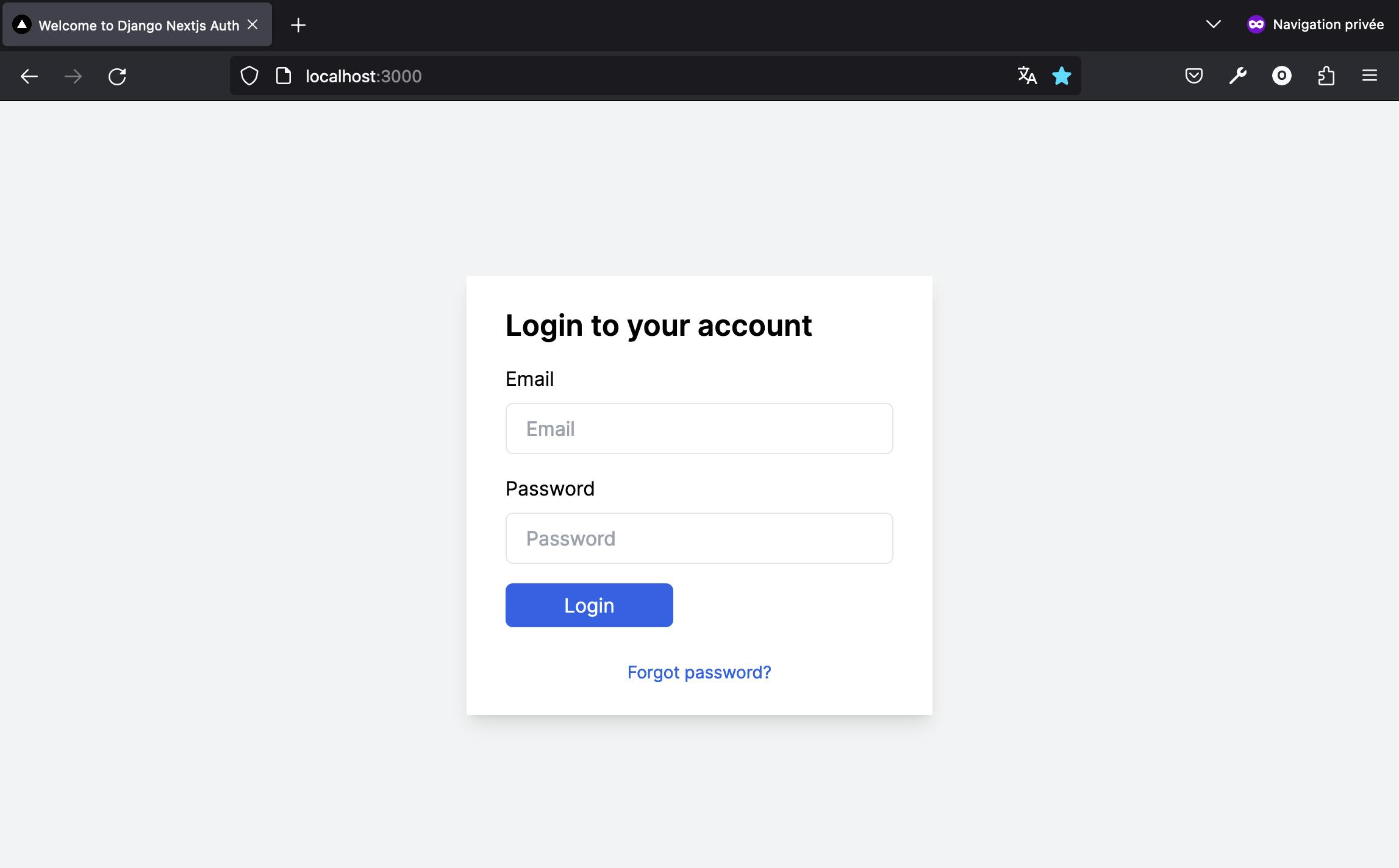
In a standard authentication process, successfully logging in will redirect the user to the dashboard page. If the login attempt fails, a message will be displayed on the form to indicate the issue, as illustrated in the authentication flow diagram below:
At this point, you might not have any users to test with, but you can create one by visiting localhost:8000/auth/users in your browser.
After creating a user, attempt to log in using the details on the Login page. You should be redirected to a page that displays an error, as shown here:
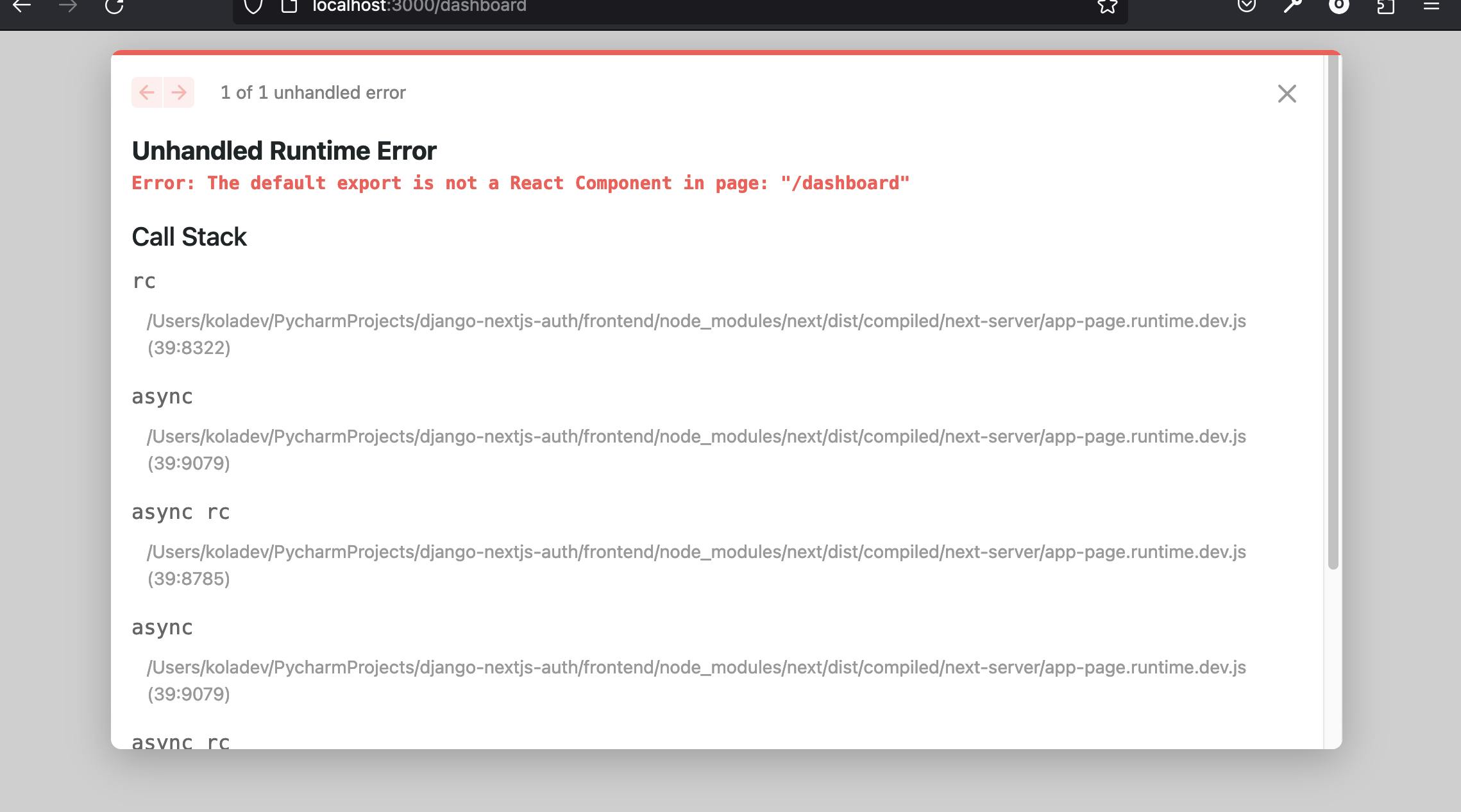
This behavior is expected because we have yet to implement the code for the dashboard/page.tsx file, which is currently empty. In the upcoming section, we will develop the dashboard home page. This page will utilize the fetcher method alongside swr and will also feature a logout button to manage user logout.
Building the dashboard home page
In the last section, we have successfully built the login page. However, the redirection to the dashboard page was not working, because well we have yet to implement the code for the dashboard page.
Let's start by opening the dashboard/page.tsx file and add the following code.
"use client";
import useSWR from "swr";
import { fetcher } from "@/app/fetcher";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
export default function Home() {
const router = useRouter();
const { data: user } = useSWR("/auth/users/me", fetcher);
const { logout, removeTokens } = AuthActions();
const handleLogout = () => {
logout()
.res(() => {
removeTokens();
router.push("/");
})
.catch(() => {
removeTokens();
router.push("/");
});
};
...
}
In the Home component for the Next.js application, we've crafted a solution to seamlessly handle user authentication, session management, and secure data fetching. Here's how we've structured it:
Extraction of Authentication Functions: We begin by extracting essential functions like
handleJWTRefresh,storeToken, andgetTokenfrom theAuthActionsutility. These are crucial for managing JWT tokens within our application.Initialization of Client-Side Navigation: We then use
useRouterfrom Next.js to enable programmatic navigation, ensuring we can redirect users to the login page if their session expires or if they're not yet authenticated.Data Fetching with SWR: We employ
useSWRalongside ourfetcherfunction for fetching the current user's data. This hook not only simplifies data fetching but also ensures that user data is kept up-to-date and secure.Logout Implementation: We define a
handleLogoutfunction that orchestrates the logout process, utilizing thelogoutmethod fromAuthActions. This function ensures that upon logout, user tokens are properly cleared and the user is redirected to the login page, maintaining a secure and clean state.Error Handling on Logout: In scenarios where the logout process encounters errors, we ensure to catch these errors, clean up by removing tokens, and redirect the user, thus guaranteeing the user is always left in a predictable state.
Let's add the JSX code representing the UI.
export default function Home() {
...
return (
<div className="min-h-screen bg-gray-100 flex flex-col items-center justify-center">
<div className="bg-white p-6 rounded-lg shadow-lg w-1/3 text-center">
<h1 className="text-2xl font-bold mb-4">Hi, {user?.username}!</h1>
<p className="mb-4">Your account details:</p>
<ul className="mb-4">
<li>Username: {user?.username}</li>
<li>Email: {user?.email}</li>
</ul>
<button
onClick={handleLogout}
className="bg-red-500 text-white px-4 py-2 rounded hover:bg-red-700 transition-colors"
>
Disconnect
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}
With the code above, we aim to display information about the user such as the username and the email, and also make the logout button available for click. Here is what you should be seeing at localhost:3000.
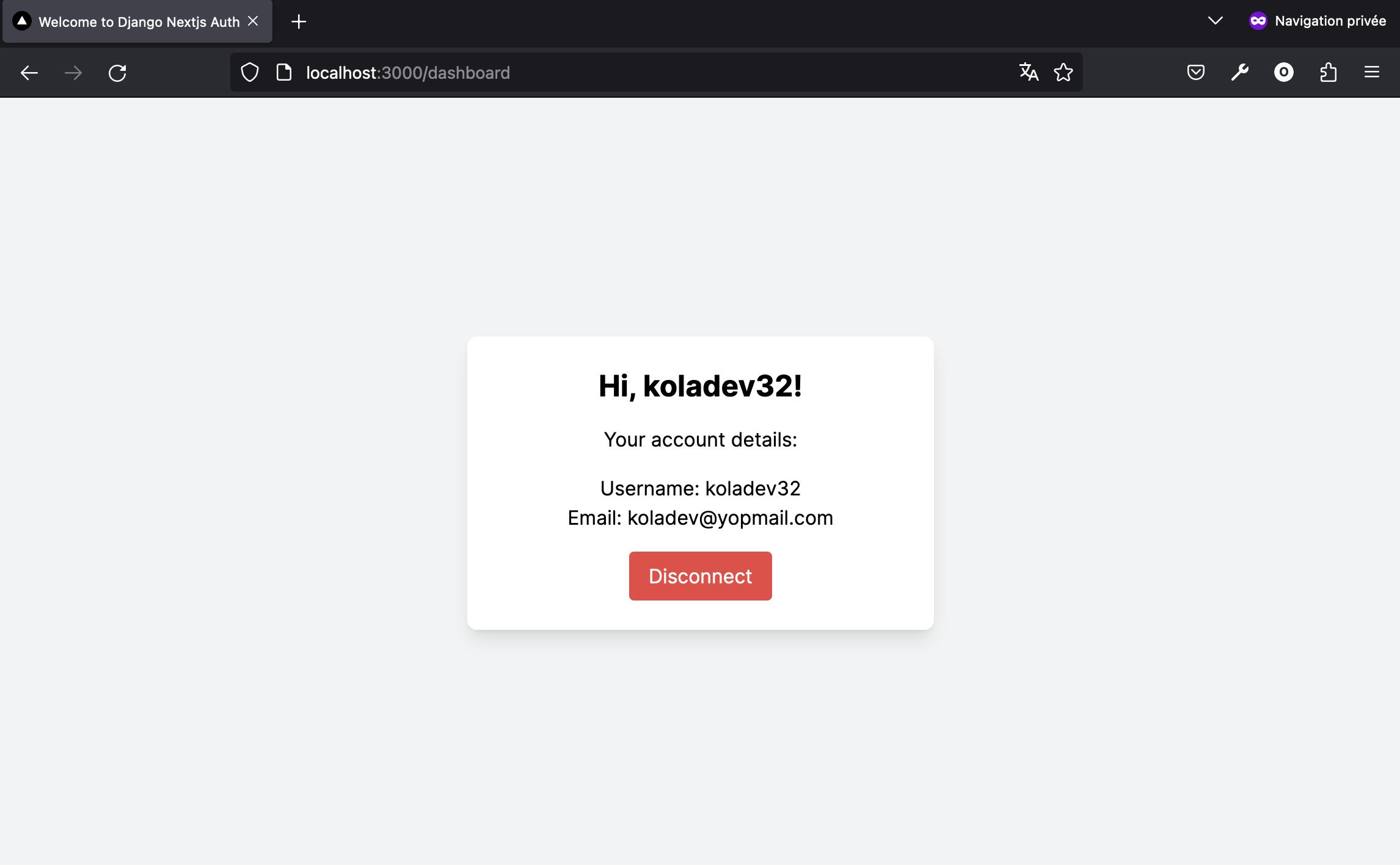
A click on the Disconnect button will remove the tokens from the cookies and the user is redirected to the login page.
To prevent unauthorized access to certain pages like the dashboard, our approach involves making a server request to check the user's authentication status. If the check fails, we then redirect the user. Ideally, it would be more efficient to verify the presence of authentication tokens before making any server request. If these tokens are missing, indicating that the user isn't logged in, we direct them to the login page immediately. This preemptive check enhances both security and user experience by avoiding unnecessary server requests.
Next.js offers a sophisticated solution to streamline this process with its AppRouter architecture, particularly through the use of middleware. Middleware allows us to execute checks on the server side before the page even starts to load. By creating a middleware.ts file in your project's src/middleware.ts directory, you can implement logic to verify authentication tokens early in the request process.
// src/middleware.ts
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import type { NextRequest } from "next/server";
import { cookies } from "next/headers";
export function middleware(request: NextRequest) {
const cookieStore = cookies();
const accessToken = cookieStore.get("accesssToken");
if (!accessToken && request.nextUrl.pathname !== "/") {
return NextResponse.redirect(new URL("/", request.url));
}
}
export const config = {
matcher: ["/((?!api|auth|_next/static|_next/image|.*\\.png$).*)"],
};
In the middleware.ts file, we implement middleware to manage authentication redirects based on cookie-stored access tokens. Here's the structured explanation:
Middleware Setup: We import
NextResponseandNextRequestfromnext/server, along withcookiesfromnext/headers, enabling us to manipulate responses, requests, and cookies in our Next.js middleware.Access Token Retrieval: A
cookieStoreis created using thecookies()method, from which we try to retrieve an "accesssToken" (noting a typo; it should likely be "accessToken"). This token is key to determining the user's authentication status. Notice that here, we are not using the methods we have written to retrieve tokens from the cookies usingjs-cookies. This is because wejs-cookiesis a function that runs on the client side, and the middleware feature of Next.js runs on the server side. Thankfully, cookies are sent to the server, thus allowing us to do some checks and ensure the user is authenticated.Unauthenticated User Redirect: In the absence of an access token, and if the request's pathname is not the login page (
/), we redirect the user to the login page. This mechanism prevents unauthenticated access to protected routes, directing users without an access token to the login or home page.Middleware Configuration: The
configsection with amatcherpattern specifies the routes this middleware applies to, explicitly excluding paths like API, static files, and images. This configuration ensures the middleware is only active on relevant paths, optimizing the application's performance and user flow. We ensure that in this matcher pattern, we ignoring theauthpages such as the registration page and reset password pages.
With this middleware, our Next.js application enhances security and user experience by redirecting users based on their authentication state, ensuring protected content remains secure and accessible only to authenticated users.
We have successfully built the Login page leading to the dashboard home page if authenticated. On the dashboard home page, we display information about a user but also display a logout button, which if clicked redirects the user to the login page.
In the next section, we are going to build the registration page.
Building the Registration page
In the last section, we have built a dashboard home page. In this section, we are going to build the registration page.
If a registration is made, we redirect the user to the login page so we can access the dashboard page.
In the src/app/components/Register.jsx file, add the following lines of code:
// src/app/components/Register.tsx
import React from "react";
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
import { useRouter } from "next/navigation";
type FormData = {
email: string;
username: string;
password: string;
};
const Register = () => {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
setError,
} = useForm<FormData>();
const router = useRouter();
const { register: registerUser } = AuthActions(); // Note: Renamed to avoid naming conflict with useForm's register
const onSubmit = (data: FormData) => {
registerUser(data.email, data.username, data.password)
.json(() => {
router.push("/");
})
.catch((err) => {
setError("root", {
type: "manual",
message: err.json.detail,
});
});
};
...
};
export default Register;
In the Register component within the Next.js application, we construct a user registration form employing the react-hook-form library for handling form state and validations, alongside integrating with AuthActions for executing the registration process. Here's a succinct overview of its configuration:
Integrating
react-hook-form: We initiate the form withuseForm, specifyingFormDatafor strong typing of form inputs such as email, username, and password. This ensures proper handling and validation of user input.Navigation with Next.js Router: Using
useRouterfrom Next.js enables us to navigate users post-registration, allowing for dynamic routing to the homepage or login page following successful account creation.Auth Actions Integration: By destructuring
AuthActions, we gain access to theregisterfunction essential for the user registration process. To circumvent naming conflicts withuseForm'sregisterfunction, we alias it asregisterUser.Submission and Error Management: The
onSubmitfunction orchestrates the registration process, invokingregisterUserwith form data. A successful request leads to redirection using Next.js's router, while failure triggers form error feedback for the user.
Let's add the JSX for the Register component.
// src/app/components/Register.tsx
const Register = () => {
...
return (
<div className="flex items-center justify-center min-h-screen bg-gray-100">
<div className="px-8 py-6 mt-4 text-left bg-white shadow-lg w-1/3">
<h3 className="text-2xl font-semibold">Register your account</h3>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)} className="mt-4">
<div>
<label className="block" htmlFor="email">
Email
</label>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Email"
{...register("email", { required: "Email is required" })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.email && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">
{errors.email.message}
</span>
)}
</div>
<div className="mt-4">
<label className="block" htmlFor="username">
Username
</label>
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Username"
{...register("username", { required: "Username is required" })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.username && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">
{errors.username.message}
</span>
)}
</div>
<div className="mt-4">
<label className="block" htmlFor="password">
Password
</label>
<input
type="password"
placeholder="Password"
{...register("password", { required: "Password is required" })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.password && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">
{errors.password.message}
</span>
)}
</div>
<div className="flex items-center justify-between mt-4">
<button className="px-12 py-2 leading-5 text-white transition-colors duration-200 transform bg-blue-600 rounded-md hover:bg-blue-700 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-700">
Register
</button>
</div>
{errors.root && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">{errors.root.message}</span>
)}
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Register;
With the JSX written, we can now move to adding the Register component to the src/app/auth/register/page.tsx file.
// src/app/auth/register/page.tsx
"use client";
import Register from "@/app/components/Register";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main>
<Register />
</main>
);
}
With the Register component imported into the page, when navigating to the localhost:3000/auth/register/ page, you will have the following display.
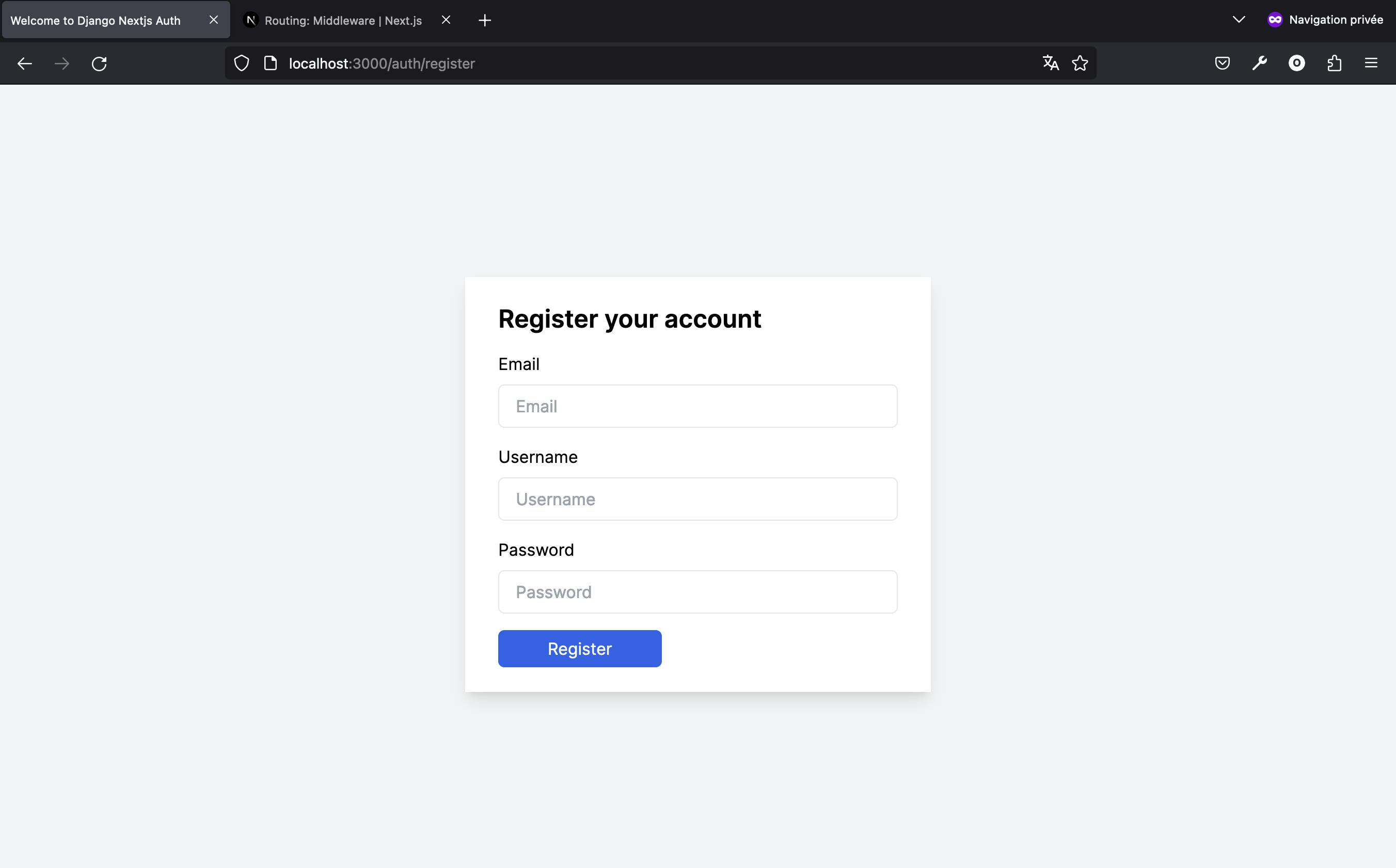
Having crafted the registration page, we've now ensured users can successfully create an account. Upon completion, they're directed to the login page where they can sign in with their new credentials. Next, we'll focus on developing the password reset feature, a crucial aspect of any authentication system.
Building the password reset feature
After setting up the registration page, our next step is to develop the reset password feature. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how the reset password process works:
Email Submission: The user begins by entering their email address on the reset password page. We then send a request to the
/users/reset_password/endpoint. This endpoint is responsible for dispatching emails for password reset. If the submitted email address matches an existing user in the database, an email is dispatched to that address. If there's no user associated with the provided email, we do nothing and fail silently — it's unnecessary and less secure to inform the user that the email address isn't found in our database.Reset Password Email: The email sent to the user includes a link to reset their password. This link redirects the user to a specific URL designed for completing the password update process. The format of this URL is
http://localhost:3000/auth/password/reset-password-confirmation/?uid={uid}&token={token}. Upon visiting this link, we'll extract theuidandtokenfrom the URL in the browser, which are essential for verifying the user's identity and proceeding with the password reset.
With a clear understanding of the reset password workflow, we're now ready to implement this feature, starting with the reset password page's code.
In the src/app/components/ResetPassword.tsx, add the following code.
// src/app/components/ResetPassword.tsx
import React from "react";
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
type FormData = {
email: string;
};
const ResetPassword = () => {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm<FormData>();
const { resetPassword } = AuthActions();
const onSubmit = async (data: FormData) => {
try {
await resetPassword(data.email).res();
alert("Password reset email sent. Please check your inbox.");
} catch (err) {
alert("Failed to send password reset email. Please try again.");
}
};
...
};
export default ResetPassword;
In the ResetPassword component, we implement the functionality for users to initiate a password reset process. This component is part of our Next.js application and uses the react-hook-form library for form management, along with our custom AuthActions for authentication processes. Here's a breakdown of its setup and functionality:
Form Setup with
react-hook-form: We usereact-hook-formto handle the form where users can submit their email addresses to request a password reset. TheuseFormhook is initialized with theFormDatatype to ensure the form data is correctly managed and validated.Integration with Authentication Actions: We access the
resetPasswordfunction fromAuthActionsto handle the password reset request. This integration allows us to manage authentication actions cohesively within our application.Form Submission Handling: When the form is submitted, the
onSubmitfunction is triggered. It sends the user's email to theresetPasswordfunction. If the request is successful, the user is alerted that a password reset email has been sent to their inbox. In case of failure, an error alert informs the user that the email could not be sent.
Let's write the JSX code for the UI.
// src/app/components/ResetPassword.tsx
...
const ResetPassword = () => {
...
return (
<div className="flex items-center justify-center min-h-screen bg-gray-100">
<div className="px-8 py-6 mt-4 text-left bg-white shadow-lg w-1/3">
<h3 className="text-2xl font-semibold">Reset Password</h3>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)} className="mt-4">
<label className="block" htmlFor="email">
Email
</label>
<input
type="email"
placeholder="Enter your email"
{...register("email", { required: true })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.email && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">Email is required</span>
)}
<div className="flex items-center justify-between mt-4">
<button className="px-12 py-2 leading-5 text-white transition-colors duration-200 transform bg-blue-600 rounded-md hover:bg-blue-700 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-700">
Send Reset Email
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default ResetPassword;
Now, in the src/app/auth/password/reset-password/page.tsx, import the ResetPassword component.
"use client";
import ResetPassword from "@/app/components/ResetPassword";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main>
<ResetPassword />
</main>
);
}
With the ResetPassword component imported into the page, when navigating to the localhost:3000/auth/password/reset-password/ page, you will have the following display.
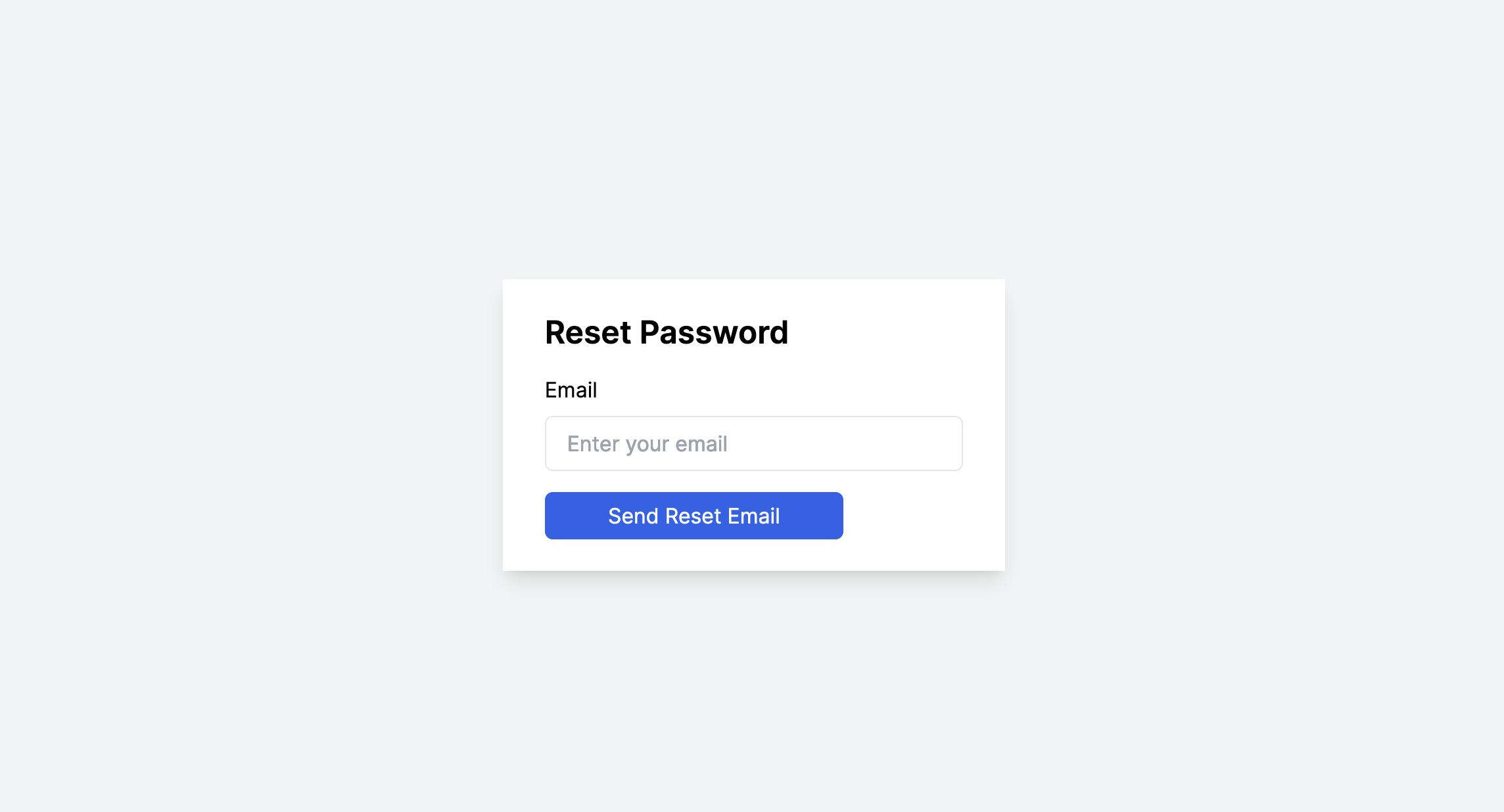
When you enter the mail, you will receive the mail in the Django console where the code is running.
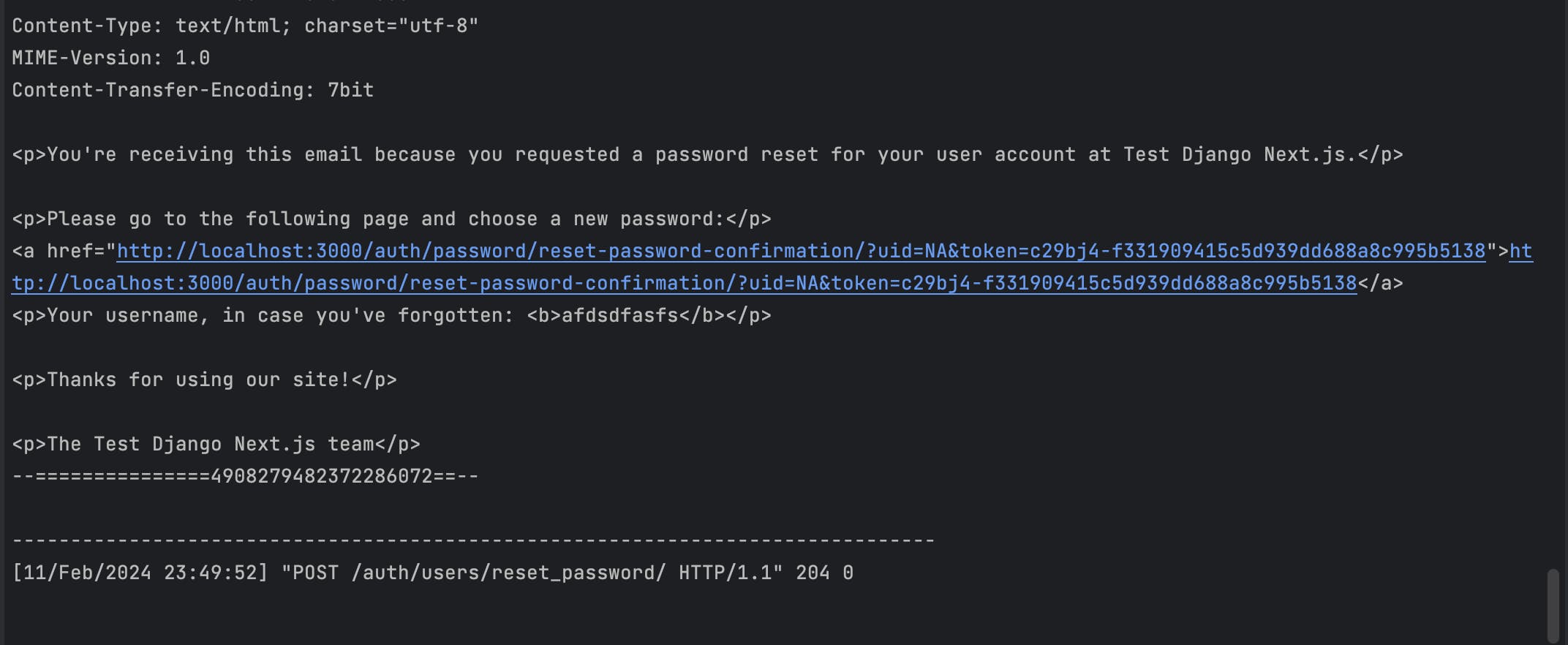
The password reset process includes a crucial step where the user, after receiving the reset email, is redirected to a specific URL to complete the password update. The URL follows this format: http://localhost:3000/auth/password/reset-password-confirmation?uid={uid}&token={token}. To accommodate this step, it's essential to create a corresponding page within our application, known as the reset password confirmation page.
This page will be responsible for capturing the uid and token parameters from the URL, which are necessary for validating the password reset request and securely updating the user's password. In the src/app/components/ResetPasswordConfirm.tsx file, add the following lines.
// src/app/components/ResetPasswordConfirm.tsx
import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
import { AuthActions } from "@/app/auth/utils";
import { useSearchParams, useRouter } from "next/navigation";
type FormData = {
password: string;
};
const ResetPasswordConfirmation = () => {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
} = useForm<FormData>();
const router = useRouter();
const { resetPasswordConfirm } = AuthActions();
const searchParams = useSearchParams();
// State for UID and Token
const [uid, setUid] = useState("");
const [token, setToken] = useState("");
// Extract UID and Token from URL
useEffect(() => {
if (searchParams.get("uid") && searchParams.get("token")) {
setUid(searchParams.get("uid") as string);
setToken(searchParams.get("token") as string);
}
}, [searchParams]);
const onSubmit = async (data: FormData) => {
try {
await resetPasswordConfirm(
data.password,
data.password,
token,
uid,
).res();
alert("Password has been reset successfully.");
router.push("/");
} catch (err) {
alert("Failed to reset password. Please try again.");
}
};
...
};
export default ResetPasswordConfirmation;
In the ResetPasswordConfirmation.tsx component of our application, we create the interface for users to finalize their password reset process. This component is crucial for securely updating a user’s password following the receipt of a reset email. Here’s how we construct and operate this feature:
Form Management with
react-hook-form: We leveragereact-hook-formto efficiently manage the new password input from the user, ensuring validation and handling of form state, including any errors.Use of Next.js Router and Search Params: We use
useRouterfrom Next.js that allows us to programmatically navigate users post-action. Additionally, we useuseSearchParamsto extract theuidandtokenparameters from the URL, which are essential for verifying the password reset request.State Initialization for UID and Token: Through React's
useState, we initialize and manage state variables for both theuidandtoken. These are critical for the password reset confirmation process.Extracting UID and Token: An
useEffecthook is employed to capture and set theuidandtokenfrom the URL's search parameters upon component mounting. This ensures we have the necessary data to authenticate the password reset request.Handling Form Submission: On form submission, the
onSubmitfunction is activated, calling theresetPasswordConfirmmethod fromAuthActionswith the new password,uid, andtoken. Success leads to an alert confirming the password reset and a redirection to the login page. In case of an error, the user is informed of the failure to reset the password, prompting them to attempt the process again.
Let's write the JSX part of the ResetPasswordConfirm component.
// src/app/components/ResetPasswordConfirm.tsx
const ResetPasswordConfirmation = () => {
...
return (
<div className="flex items-center justify-center min-h-screen bg-gray-100">
<div className="px-8 py-6 mt-4 text-left bg-white shadow-lg w-1/3">
<h3 className="text-2xl font-semibold">Set New Password</h3>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit(onSubmit)} className="mt-4">
<label className="block" htmlFor="password">
New Password
</label>
<input
type="password"
placeholder="Enter your new password"
{...register("password", { required: true })}
className="w-full px-4 py-2 mt-2 border rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-1 focus:ring-blue-600"
/>
{errors.password && (
<span className="text-xs text-red-600">Password is required</span>
)}
<div className="flex items-center justify-between mt-4">
<button className="px-12 py-2 leading-5 text-white transition-colors duration-200 transform bg-blue-600 rounded-md hover:bg-blue-700 focus:outline-none focus:bg-blue-700">
Reset Password
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default ResetPasswordConfirmation;
Then, add this component to the src/app/auth/password/reset-password-confirm/page.tsx file.
// src/app/auth/password/reset-password-confirm/page.tsx
"use client";
import ResetPasswordConfirmation from "@/app/components/ResetPasswordConfirmation";
export default function Home() {
return (
<main>
<ResetPasswordConfirmation />
</main>
);
}
Now, then clicking a reset password link sent via email, you will have a display like this.
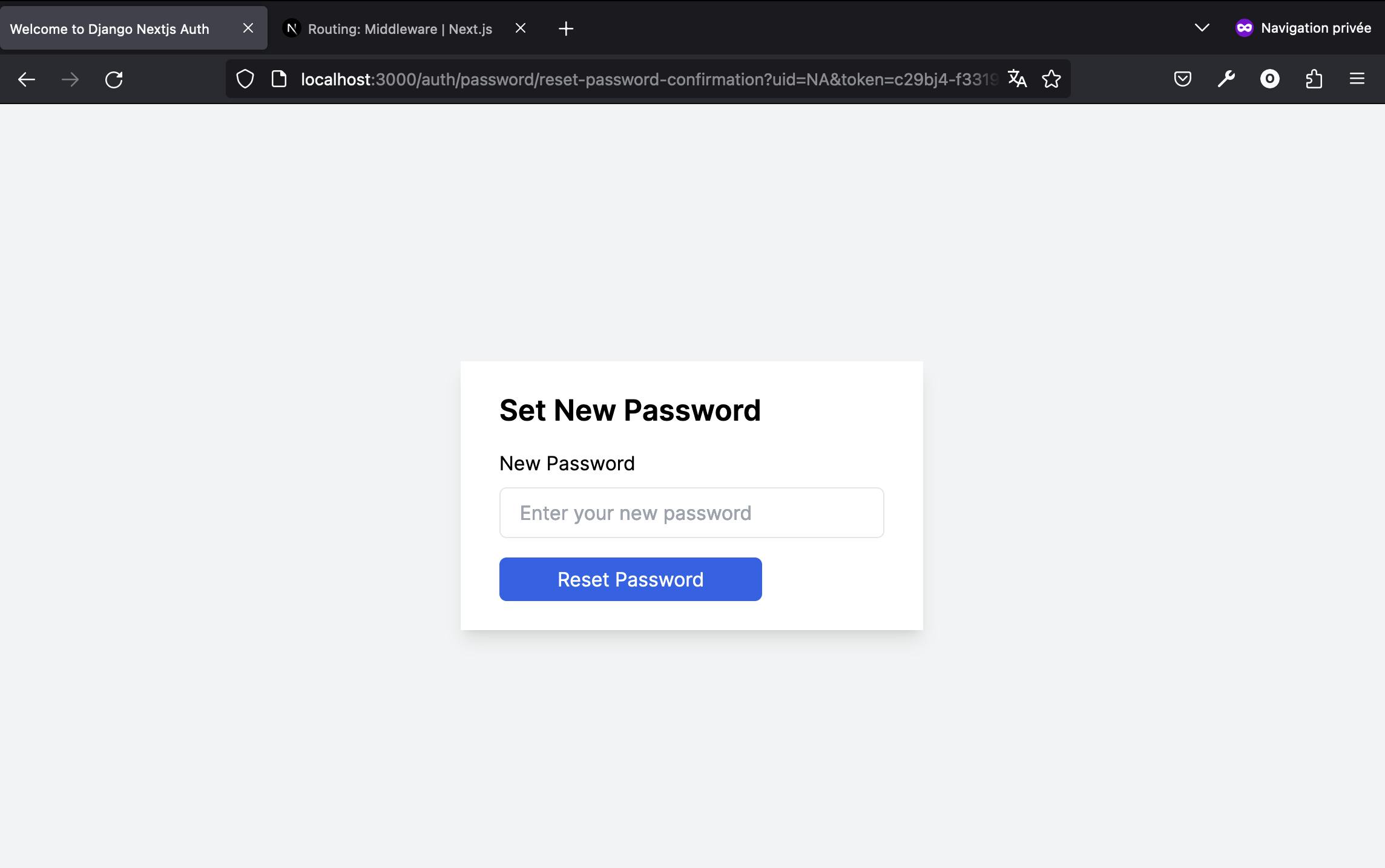
Fantastic! We've successfully established a complete password reset flow, marking the completion of our full-stack application development with Django and Next.js. Throughout this journey, users have gained the capability to register, log in, and reset their passwords when necessary.
We've explored and used powerful features from the Next.js AppRouter, demonstrating how to construct a responsive and integrated frontend that communicates effectively with the Django backend. This tutorial provides a solid foundation for anyone looking to start building applications using Next.js for the frontend and Django for the backend.
You can find the codebase for this project on Github at https://github.com/koladev32/django-nextjs-auth.
Conclusion
In this article, we built a back-end application with Django that handles authentication, including features like registration, login, and password reset to secure our back-end. For the front-end, we used Next.js and explored the AppRouter architecture, making use of the swr , wretch, react-hook-form packages to connect our front-end with the back-end. We dove into how middleware and routing from the AppRouter architecture can create an interesting application.
This guide is great if you're planning to start a project using React and Django. For those interested in incorporating Redux, I've experimented with it on a separate branch called redux in the project repository. It's not perfect, but it offers insights into integrating Redux into your application. You can check it at https://github.com/koladev32/django-nextjs-auth/tree/redux.
Looking ahead, there's a lot you can experiment with and improve. If you have questions or feedback about this article, please share them in the comments. Your input helps make this resource better for everyone. Below are the resources we used in this article.
That's all for now. Happy coding!🚀
